INTRODUCTION
Most sinus diseases occur bilaterally, and it has been reported that 2.5% to 23.1% of cases of unilateral sinusitis occur [
1,
2]. The causes of unilateral sinusitis include fungal sinusitis, cyst, malignant tumor and odontogenic sinusitis [
3]. Recently, as surgical treatment in the oral cavity has been developed and invasive dental treatment such as implantation has increased, the incidence of odontogenic sinusitis is on the rise, and there was a report that odontogenic sinusitis was found in about 40% of unilateral sinusitis [
4-
8]. Among odontogenic sinusitis, implant surgery-related cases vary from about 8% to 37% [
8-
11]. If odontogenic sinusitis is suspected due to implants, a collaboration with the dentist to check the connection to the implants and the need for implant removal is an important process of the treatment.
The purpose of this study is to report the clinical characteristics of sinusitis patients who have recently increased after implant surgery, and to investigate the points to be considered in establishing a diagnosis and treatment policy through collaboration with dentistry.
METHODS
From January 2015 to December 2019, medical records of patients who developed maxillary sinus disease after implant surgery among patients who were treated in collaboration with the Department of Otolaryngology and Dentistry at Dong-A University Hospital were retrospectively analyzed. Based on the medical records, cases where the posterior relationship between the implant procedure and symptoms did not match, and cases where the implant site did not match the position of the maxillary sinusitis were excluded, leaving the medical records of 15 patients to be analyzed. The patient’s outpatient visit and hospitalization, surgical records and the patient’s age, sex, medical history, and underlying disease were reviewed, and the physical examination and computed tomography (CT) findings were analyzed.
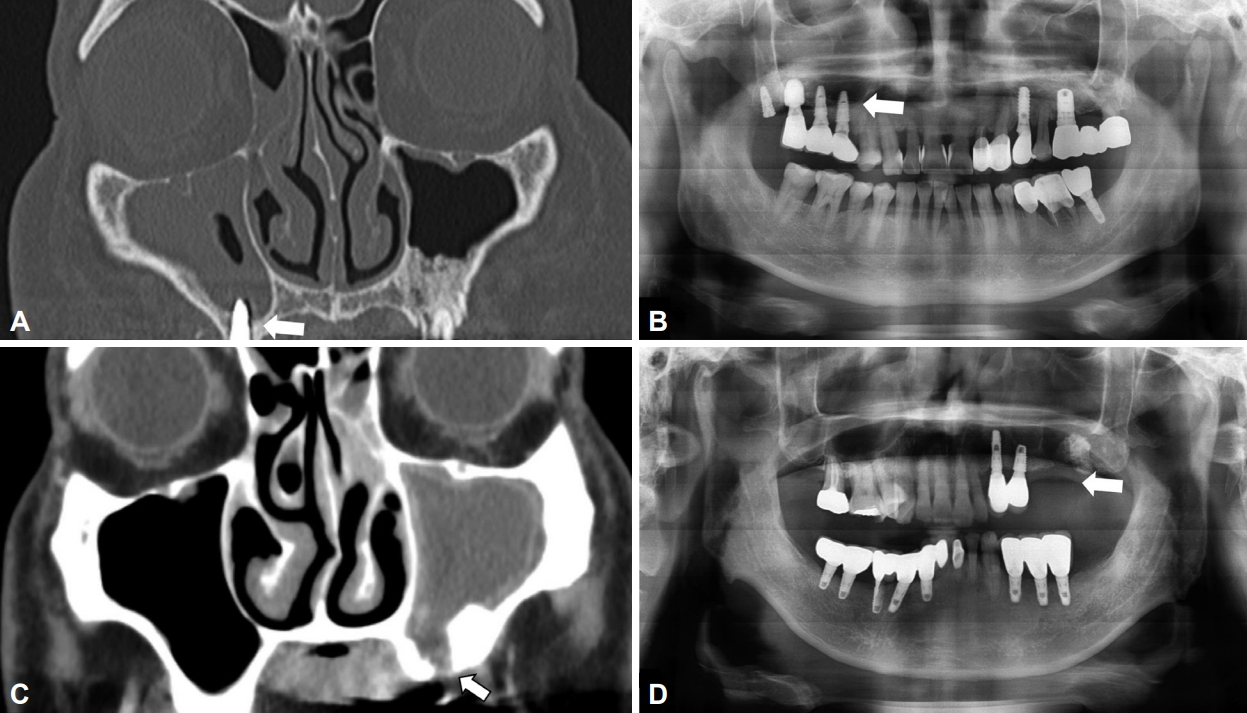
In CT images and panoramic radiology, odontogenic sinusitis such as oroantral fistula due to maxillary alveolar bone defect, sinusitis accompanied by infiltration of artificial root in the maxillary sinus, and loss of lamina dura and periapical abscess showing surrounding soft tissue shading were defined as positive findings (
Fig. 1).
If there is a history of suspected sinusitis related to the implant procedure on the interview or positive findings are observed on CT, a consultation with the dentist was requested to confirm the relationship between the sinusitis and the implant and, if necessary, to provide dental treatment. When visiting the dentist, the condition of teeth, alveolar bone, and periodontal was checked through physical examination, and panoramic radiology was taken.
The diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis is made for patients who have positive findings on CT, have symptoms suggestive of odontogenic sinusitis based on a medical history, or have the right chronological sequence for implant surgery and sinus or odontogenic symptoms, followed by an identified dental lesion through consultation with dentistry.
Patients diagnosed with odontogenic sinusitis were treated with antibiotics and dental treatment, or endoscopic sinus surgery was performed, and if necessary, surgery was performed simultaneously with the collaboration with dentistry. All patients were followed-up for at least three months to check for recurrence. This study was conducted after being reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Dong-A University Hospital (approval number: DAUHIRB 19-149).
RESULTS
Of the 15 patients, 8 (53%) were male and 7 (47%) were female, and the mean age was 57 (range; 20–77 years old). By age, 1 in their 20s (6%), 1 in their 30s (6%), 1 in their 40s (6%), 5 in their 50s (33%), 5 in their 60s (33%), and 2 in their 70s (13%). Of the 15 patients, 3 patients (20%) were smokers, and 3 patients (20%) had a history of diabetes.
There were 12 patients who had their first visit at the otolaryngology department and 3 patients had their first visit at the dentist. The main symptom complained at the first visit was facial pain in 7 patients (47%), which was the most frequent, followed by pus from the maxillary fistula on the oral side in 2 patients (13%), nasal obstruction in 2 patients (13%), rhinorrhea, post-nasal drip, headache, and asymptomatic in 1 patient respectively (6%). On CT, there were 2 cases of bilateral sinus opacity (13%) and 13 cases of unilateral sinus opacity (88%), which makes unilateral sinusitis more common cases. Eight cases were on the left side (47%) and 9 on the right side (53%). Seven patients had spread only to the maxillary sinuses, and 8 patients had spread to other sinuses including the maxillary sinuses. The CT image showed that there were 8 patients with positive supragingival sinusitis, 6 patients (40%) had an intrusion of the artificial root in the maxillary sinus, and 2 patients (13%) had an oroantral fistula.
The main diseases of the diagnosed patients were as follows: 15 cases of odontogenic rhinosinusitis (ORS), 1 case of chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps, 1 case of postoperative check cyst, and 1 case of fungal sinusitis, 1 case of inverted papilloma, and 1 case of radicular cyst. Five cases other than odontogenic sinusitis were diagnosed additionally after surgery (
Tables 1 and
2).
For the treatment of odontogenic sinusitis, endoscopic sinus surgery was performed in 14 out of 15 patients, and 1 patient improved after antibiotic treatment. Two patients underwent dental surgery along with endoscopic sinus surgery, and 1 patient underwent implant removal, and 1 patient underwent radical cyst enucleation. Of the 14 patients who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery, 3 had already had their tooth extracted. The average follow-up period after treatment was 8.6 months, and no recurrence was observed in all patients (
Tables 1 and
2).
DISCUSSION
It is known that sinusitis is caused by a ventilation disorder in the sinuses due to an intranasal disease. However, anatomically close dental diseases may spread to the sinuses, causing disease which is called odontogenic sinusitis. Among odontogenic sinusitis, the number of cases related to implant surgery varies from about 8% to 37% [
8-
11]. The causes of odontogenic sinusitis can be divided into three main categories. First, there may be a case where a route like an oral maxillary fistula occurs and the source of infection in the oral cavity goes retrograde to the sinuses. The second is when the boundary between the oral cavity and the sinuses is weakened due to an abscess around the root point, impacted teeth, periodontal disease, etc. [
12]. Thirdly, there can be an inflammation around the root canal spreads to the sinuses. Sinusitis that occurs after implant surgery may be caused by alveolar bone implants or dental implants prolapsed into the maxillary sinus, or osseointegration between the implant and the alveolar bone is not achieved, which leads to continuous oral maxillary sinus fistula and entrance of bacteria in the oral cavity into the maxillary sinus [
13-
15].
As the maxillary bone grows, anatomically, the bottom surface of the maxillary sinus is in contact with the root of the maxillary tooth with a thin bone in between, and the distance between the maxillary sinus and the root is very close to about 2.0 mm, but it is consisted of the hard cortical bone, which makes it not easy for the odontogenic infection to be spread to the sinuses [
12]. However, when damaged during invasive procedures such as tooth extraction or implant surgery, the possibility of developing odontogenic sinusitis increases.
The most common cause of odontogenic sinusitis is periodontal disease or abscess, but due to the development of oral and maxillofacial surgery, iatrogenic sinusitis is increasing in the process of manipulating various instruments or using materials used for root canal treatment. As the number of dental procedures is rapidly increasing, the frequency is on the rise as well [
10].
In otolaryngology, CT imaging of the sinuses is widely used as a diagnostic tool to differentiate dental causes. Oroantral fistula due to maxillary alveolar bone defect, sinusitis accompanied by infiltration of artificial root in the maxillary sinus, and loss of lamina dura, and periapical abscess with surrounding soft tissue shadows in CT images and panoramic radiology can be regarded as findings of odontogenic sinusitis. There are cases where patients with maxillary sinus disease that occurred after implantation do not complain of odontogenic symptoms. Therefore, it is recommendable to have them examined at dentist if a patient has a history of implants, and if the implant site and the direction of maxillary sinusitis coincide.
The treatment of maxillary sinus disease is basically the proper treatment of the lesion and prevention of recurrence. For sinusitis that occurs after implant surgery, drug treatment including empirical antibiotics, nasal washing, and sinus irrigation are performed. If there is no response to these conservative treatments, endoscopic sinus surgery should be performed. In the case of severe peri-implantitis or recurrent sinusitis, the implant must be removed during endoscopic sinus surgery, but the implant can be preserved when the sinus function is restored to normal [
16]. In most cases, removal of the lesion is possible with endoscopic sinus surgery, and maxillary sinus radical surgery is not recommended because of the high risk of isthmus cyst and complications after surgery. Since the authors’ hospital is a tertiary care institution, most of the patients visited the hospital because they did not show improvement after taking medication at other hospitals. The limitations of this study are that most of the subjects of this study were patients who received surgical treatment, and that the evaluation of patients who would have improved after drug treatment was lacked.
Moreover, in the cases of odontogenic sinusitis, anaerobic and gram-negative bacteria are found in the oropharynx in addition to the usual
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and
Moraxella catarrhalis, which makes it hard to be treated with antibiotics [
17]. Decision on which antibiotic to use is based on bacterial test in principle, but due to practical matters, antibiotics are selected in stages. Usually, antibiotics are used for less than four weeks [
18].
Although surgical removal of the odontogenic infection source is important to treat odontogenic sinusitis, it is not necessary to remove the implant in all cases of odontogenic sinusitis after implantation. It is necessary to decide whether or not to remove the artificial tooth through cooperation with the dentist considering various conditions of artificial teeth, such as the state of the bone graft in the maxillary sinus around the implant, the degree of exposure of the implant thread, and the degree of invasion of the implant into the maxillary sinus. In this study, except for one patient, the lesion was successfully removed only by endoscopic sinus surgery without removing the implant, and there was no recurrence. The patient who had the implant removed underwent the procedure because it was determined that it would be difficult to maintain the implant due to the situation of the implant and alveolar bone during dental treatment.
In conclusion, the authors suggest that when a patient with maxillary sinus disease visits the hospital, collaboration with the dentist is necessary provided that the location of the maxillary sinus disease and the implant procedure match, the manifestation of the maxillary sinus disease and the implant procedure are in the correct chronological order, and there are significant findings on CT of the sinus. In some cases, there are patients who do not complain of odontogenic symptoms. Therefore, if an implant problem is suspected through physical examination and interview, it is necessary to diagnose sinusitis after implantation through active collaboration. In addition, the study is thought to be helpful in analyzing the clinical characteristics of maxillary sinusitis after implant surgery, and it is necessary to establish a clearer treatment algorithm through additional research involving a larger number of patients.







 PDF Links
PDF Links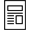 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



